The warehouse of the future is a place where shelves are organized by themselves, orders can be fulfilled in seconds, and productivity reaches unprecedented levels. Warehouse management software, such as the one you aim to build, is the secret to this transformational leap.
Are you prepared to tap into its enormous potential? This blog will guide you on a journey of vision to build warehouse management software in 2023. We’ll examine the latest techniques and trends in the industry, from integrating IoT and artificial intelligence to harnessing cloud computing and building Warehouse Management Software.
Learn how to improve your warehouse operations by integrating real-time analytics and user interfaces with seamless inventory tracking. This blog is for ambitious entrepreneurs and tech-savvy developers who want to build warehouse management software that will revolutionize your industry. Prepare to unlock the future in warehousing.
What is Warehouse Management Software & How Does It Work?
Warehouse Management Software is an automated system that assists businesses in managing and optimizing their warehouse operations. It’s designed to automate and streamline tasks such as order fulfillment, inventory management, receiving and shipping, and tracking goods within the warehouse.
If you want to build warehouse management software can revolutionize the way businesses handle these operations. Warehouse management solution integrates with other systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning software (ERP), barcode scanners, and mobile devices.
The system uses real-time information to give accurate and current information on inventory levels, the location of goods, and order status. By utilising Warehouse Management Software, businesses can make informed decisions about stock replenishment and order prioritization. They can also optimize warehouse layout by implementing the software’s suggestions.
WMS has many features, including inventory tracking. It allows businesses to track stock levels, locations and minimize stockouts. Order management is another feature of WMS, which allows businesses to manage orders efficiently and accurately, increasing customer satisfaction.
Build Warehouse Management Software; businesses can enhance their order management processes and improve customer experience. WMS also optimizes warehouse layout by suggesting optimal storage locations for various types of products based on their characteristics and demand patterns.
Top Warehouse Management Systems
| Software | Description | Rating | Downloads | Available Platforms |
| SAP Extended Warehouse Management | SAP EWM is a comprehensive solution that integrates with SAP ERP systems to manage complex warehouse operations. It offers features such as inventory tracking, order fulfillment, labor management, and advanced analytics. | 4.5/5 | Available on request | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Oracle Warehouse Management | Oracle WMS is a scalable and flexible solution that optimizes warehouse processes. It offers features like inventory control, labor management, wave planning, and integration with other Oracle applications. | 4.4/5 | Available on request | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Manhattan Associates Warehouse Management System | Manhattan WMS is a robust solution designed for large-scale warehouses and distribution centers. It offers advanced features such as automation control, slotting optimization, labor management, and real-time visibility. | 4.6/5 | Available on request | Windows, Linux |
| JDA Warehouse Management | JDA WMS is a feature-rich solution that provides end-to-end visibility and control over warehouse operations. It includes features like inventory management, order fulfillment, labor optimization, and integration capabilities. | 4.3/5 | Available on request | Windows, Linux |
| Blue Yonder Warehouse Management | Blue Yonder WMS (formerly JDA WMS) is a cloud-based solution that helps streamline warehouse operations with advanced automation, optimization algorithms, and real-time visibility. | 4.7/5 | Available on request | Windows, Linux |
Types Of Warehouse Management Systems
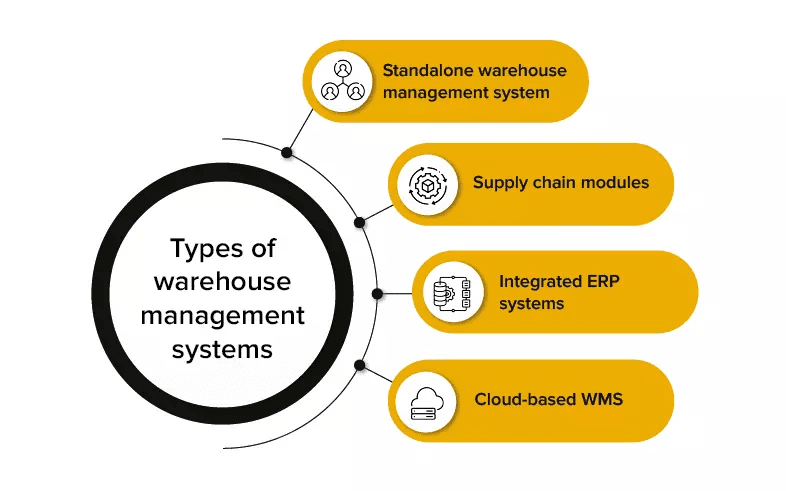
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are software programs that optimize and manage the operation of a distribution centre or warehouse. Build Warehouse Management Software Warehouse Management Systems come in several types, each with capabilities and features. Here are a few common types.
1. Standalone WMS
Build Warehouse Management Software Standalone WMS (or standalone software) is a traditional on-premises system that runs on local servers. It offers comprehensive functionality, such as inventory management, order fulfilment, picking, packing, and shipping. Standalone WMS offers many advanced features and is highly customizable but requires a significant IT infrastructure.
2. Cloud-based WMS:
Build Warehouse Management Software Cloud-based WMS is accessible online and operates on remote servers. It provides the same functionality as standalone WMS but does not require on-site server infrastructure. Cloud-based WMS are scalable, flexible, and available as a subscription-based service, making them popular with small and medium-sized businesses.
3. Integrated WMS
Build Warehouse Management Software The integrated WMS integrates seamlessly with other enterprise software, such as Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (ERP) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). It allows real-time data sync and collaboration across departments to improve visibility and efficiency.
4. Open-Source WMS:
Build Warehouse Management Software Open-source WMS is a term used to describe software systems available for free that can be customized and modified by users. Often, a community of developers is actively involved in improving and customising these systems. The open-source WMS is flexible and offers savings but may require technical knowledge to maintain and implement.
5. WMS with Labor Management
Build Warehouse Management Software Some WMS solutions come with labour management features, which allow businesses to optimize the performance of their workforce within the warehouse. These warehouse inventory management solutions offer insights into labour productivity and workload balancing. They also provide performance-based incentive programs that help improve efficiency and lower labour costs.
6. Mobile WMS:
Build Warehouse Management Software Mobile WMS uses mobile devices like smartphones and tablets to perform warehouse tasks. Staff can use mobile apps to pick up, pack, and ship products while capturing data live. Mobile WMS improves flexibility and accuracy while reducing paperwork.
7. Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI WMS):
Build Warehouse Management Software VMI WMS was designed specifically for vendor-managed inventories, in which the supplier manages inventory levels at the customer’s warehouse. These systems allow suppliers to monitor stock and make replenishment and delivery decisions based on predefined agreements.
15 Features of Warehouse Management Software
WMS plays an important role in improving warehouse operations. It streamlines warehouse operations by automating various processes such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and tracking. We will examine 15 features that are essential to building the best warehouse management solution in this section.
1. Inventory Management:
WMS gives warehouse managers real-time visibility of inventory levels. This allows them to accurately track stock levels. It allows for efficient stock replenishment and reduces stockouts.
2. Order Management:
Automated order processing is possible, from the creation of orders to their fulfilment. The Warehouse Management Software ensures that orders are picked, packed, and shipped accurately, which reduces errors and improves customer satisfaction.
3. Warehouse Mapping
WMS provides a graphic representation of the layout of your warehouse, including aisles and racks. This feature makes it easier to locate products and optimize the use of space.
4. Barcoding and Scanning
WMS integrates barcode scanners, mobile devices, and other software to provide efficient barcode scanning. This is useful for tracking inventory, verifying orders, and identifying products. It speeds up operations and reduces errors.
5. RFIDs and IoT integration:
Advanced Warehouse Management Software systems use RFID (Radio Frequency ID) and IoT technologies for real-time inventory tracking. This feature improves inventory accuracy and allows for automated tracking and monitoring.
6. Batch and Lot Tracking:
WMS provides traceability along the entire supply chain, which helps manage products with batch or lot numbers. It allows for efficient recalls and ensures that regulations are followed.
7. Cycle Counting:
The warehouse inventory management software can perform a cycle count instead of a physical inventory. It involves counting subsets of items regularly. It improves inventory accuracy while minimizing disruptions in daily operations.
8. Returns Management:
WMS allows for efficient returns processing, from receipt to restocking and disposition. It makes sure that all returned items are correctly accounted for, and it reduces the amount of time spent on handling returns.
9. Cross-Docking:
This feature allows the transfer of goods directly from the inbound shipment to the outbound shipment without any storage. This feature reduces handling costs and expedites order fulfilment. It also improves efficiency.
10. Automated Replenishment:
WMS generates automatic replenishment tasks using predefined rules. It ensures the correct products are available when needed, minimizing stockouts and optimizing inventory.
11. Pick and Pack Optimization:
It optimizes the order picking and packing process by suggesting the most efficient routes for picking and packaging. It minimizes mistakes, reduces travel times, and speeds up order fulfilment.
12. Real-time Reporting And Analytics:
WMS gives real-time insight into KPIs such as order fulfilment rates and cycle times. It allows for data-driven decisions and identifies improvement areas.
13. Integration with Other Systems:
WMS can be integrated with other business software such as enterprise resource planners (ERP), transportation management systems (TMS), or e-commerce platforms. It provides seamless data flows and complete visibility throughout the supply chain.
14. Automating Workflows:
WMS automates repetitive processes, like receiving, putting away, and ordering, which reduces manual effort and improves productivity. The warehouse staff can focus more on value-added tasks.
15. Scalability and flexibility:
Warehouse management solutions should be flexible and scalable enough to adjust to changes in the warehouse. It should be able to handle multiple warehouses and different product types and fulfilment methods.
How to Build Warehouse Management Software in 2023?

To ensure project success, careful planning and coordination are required. This process is crucial since mobile app development company are responsible for designing, developing, and implementing the software. This guide will explain the steps to building warehouse management software, including hiring developers to build warehouse management software.
1. Define Your Needs:
Begin by identifying your specific requirements and goals for your warehouse management software. Consider inventory management, tracking orders, reporting, integration requirements, and user interface. You can communicate your requirements to the developers you hire to build warehouse management software.
2. Prepare a Detailed Project Brief:
Create a detailed project brief outlining the software’s objectives, scope, and technical requirements. Include any features or functionalities you wish to include. It will act as a guide for developers throughout the development process of building warehouse management software.
3. Find the Right Developer:
Hire dedicated developers with experience building enterprise-level applications and knowledge in relevant technologies like cloud computing, database management, and front-end design. Depending on your budget, you may want to consider hiring an in-house development team or outsourcing the project to build warehouse management software.
4. Interviews And Portfolio Evaluation:
Interviewing potential developers will allow you to evaluate their technical, problem-solving, and communication abilities. Examine their portfolios and see if they align with your vision of the warehouse software. Consider to hire mobile app developers to build warehouse management software.
5. Collaboration On the Development Plan:
Create a detailed plan of development in close collaboration with developers. This plan should include milestones and deliverables for each phase. Ensure your plan is realistic, achievable, and within time and budget constraints to build warehouse management software.
6. Agile Development Approach:
Consider using an agile methodology such as Scrum, Kanban, or Kanban. These methods encourage iterative development and allow for frequent feedback. This method ensures software is developed incrementally with frequent opportunities to review the functionality of warehouse management software.
7. Communication And Tracking of Progress:
Keep the lines of communication open with the team during the entire project. Regular meetings are held to review progress, discuss challenges or concerns, and give feedback. You can stay informed, and the project will remain on track in building warehouse management software.
8. Testing And Quality Assurance:
Set up a robust process for quality assurance to ensure that the software meets desired standards. Testing the software during different stages of development will help identify any bugs and issues. User acceptance testing involves end users and collects feedback about the usability and functionality of warehouse management software.
9. Deployment of Troops And Training:
Deploy the software in your warehouse once it is complete. Your staff should be trained to become familiar with the features and functions of the new software. It will ensure a smoother transition and maximum warehouse management software user adoption.
10. Maintenance And Support:
Establish a plan to maintain and support the software after it is installed. Update the software regularly to fix or improve any problems, and offer technical support for user questions or problems. Ensure maintenance and support of warehouse management software.
How Much Does It Cost To Build Warehouse Management Software?
Building warehouse management software costs vary widely depending on several factors related to the Build Warehouse Management Software.
These include the complexity of the software, its features and functionality for building warehouse management software, the technology stack used, the location of the development team involved in building warehouse management software, and the degree of customization required.
The following is a breakdown of the cost components typically involved in developing warehouse management software for building warehouse management software.
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range |
| Planning and Analysis | Gathering requirements, system design, and documentation | $1,000 – $3,000 |
| Development | Front-end and back-end development | $3,000 – $5,000+ |
| Database Design | Designing the database structure and schema | $4,000 – $6,000 |
| Third-Party Integrations | Integrating with external systems (e.g., ERP, CRM) | $3,000 – $7,000+ |
| User Interface Design | Designing the user interface and user experience | $5,000 – $7,000+ |
| Testing and Quality | Quality assurance, bug fixing, and testing | $3,000 – $6,000+ |
| Deployment and Launch | Preparing for deployment and launching the software | $4,000 – $5,000+ |
| Maintenance and Support | Ongoing maintenance, updates, and technical support | $8,000 – $25,000+ per year |
Please be aware that these ranges of costs are only approximate and may vary significantly depending on the factors listed above. However, the actual cost to build warehouse management software may vary from $8,000 to $25000 and more. To get an accurate estimate, you should consult with software firms or consultants.
In A Nutshell!
To conclude, building warehouse management software for 2023 will require careful planning, collaboration, and cutting-edge technology. The key steps are defining the scope of the software, gathering requirements, and designing an intuitive interface.
Integrating hardware, such as barcode readers and IoT devices, is essential for real-time data gathering. Cloud computing and data analysis also enable advanced reporting and optimization. Following these guidelines will help businesses develop efficient and powerful warehouse management software that is tailored to their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How Can I Begin Building Warehouse Management Software By 2023?
Start by gathering requirements, designing the system architecture, selecting a technology stack, and creating a development strategy. Focus on scalability and real-time tracking of data, as well as intuitive user interfaces.
Q2. What Features Should My Warehouse Management Software Include?
The essential features are inventory management, order processing, and barcode scanning. They also include real-time analytics, task planning, automated data collection, real-time analysis, real-time analytics, and integration with other systems such as ERP or CRM.
Q3. What Programming Languages Would Be Best For Developing Warehouse Management Software?
In 2023, Python, Java C#, and JavaScript will be the most popular languages to develop warehouse management software. Select a language that is compatible with the skills of your team and the requirements for the project.
Q4. How Can I Ensure Data Security In My Warehouse Management Software?
Update and patch your software regularly to fix security vulnerabilities. Implement secure authentication methods, encrypt sensitive information, restrict access according to user roles, and update and patch it. Conduct regular penetration tests and security audits.
Q5. How Long Does It Usually Take To Develop Warehouse Management Software?
The timeline for development varies depending on the project complexity and size of the team. It can take from several months to an entire year to develop a complete warehouse management solution. Customization requirements and integration difficulties can cause the timeline to be extended.